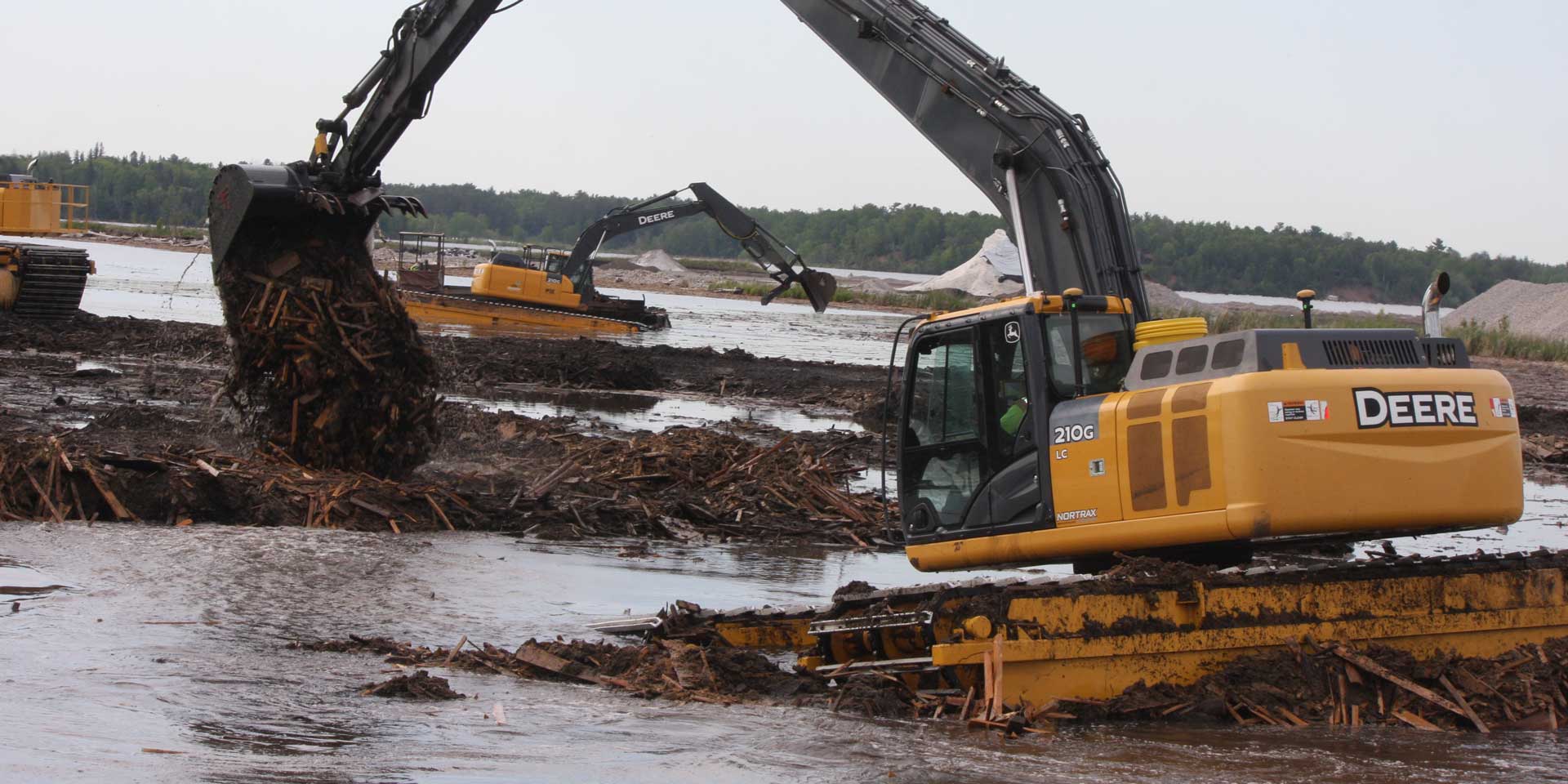
Over the years, contractors involved in underwater excavation projects — dredging, pond/lake expansions, creation of boat landings, waterfront cleanups, etc. — have become some of the most ardent supporters of GNSS-based solutions. They’ve found that the ability to “see” beneath the surface with their machines has proven invaluable in improving overall efficiency and minimizing the risk of over/under cutting. For Midwest Amphibious Equipment, making the move to GPS on two of its specialty excavators is doing precisely that, as the company tackles a huge restoration project on the waterfront in Duluth, Minnesota. Along with its newfound productivity, the company has found that incorporating the new solution will open the door to additional work, much of which had previously evaded them. It would seem to be the gift that keeps on giving.

"In the late 1800s, this part of the waterfront was the home to a couple of sawmills and, as was common in those days, cuttings from the mills’ operations ended up in the river."
CEO Steve Gilbertson, Midwest Amphibious Equipment (MAE)
Banking on It
Although they bring decades of expertise to the job site, Midwest Amphibious Equipment (MAE), as a company, has only been working the shallows for about five years. According to CEO Steve Gilbertson, their origin stems from an unlikely source.
“Up until about five years ago, I was doing similar work for an equity firm that specializes in wetland mitigation banks around the U.S.,” he said. “That company had landed a project to handle restoration of 23,000 acres in an area known as the Sax-Zim Bog in northern Minnesota. After years of work to get the project permitted, it was finally approved, at which point the head of operations and I looked at each other and began considering the best way to remediate 36 sq. mi. of bog that we couldn’t walk across. He suggested we look into a company from Louisiana that manufactures amphibious excavators — machines with pontoons that thrive in the swamps so common down there. I did, and quickly learned that they are very expensive, both to purchase and to move.”
According to Gilbertson’s calculations, in the course of that three-year project, they would have racked up about $2.5 million in mobility charges alone. Seeing that as bordering on overkill and knowing that potential swamp and bog work can also be plentiful in north central Minnesota, he opted instead to purchase the machines himself — and MAE was born.
“At the bog, we showed the benefits we can bring to the project, ” he said. “Our big selling point is that we can get into places others can’t. We can literally unload off a truck, go to the middle of nowhere, do what needs to be done and move on to the next job. It’s a nice capability to have and provide. And, as a result of that job, we are now breaking into other markets, including regional utilities, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources (DNR).”

Digging Up the Past
With the Sax-Zim job under their belts, MAE was primed for additional work and quickly landed it in a DNR-led effort to remediate a section of the St. Louis River on the waterfront in Duluth, Minn. As part of a larger project to restore more than 1,700 acres of the area’s Grassy Point and Kingsbury Bay, MAE, working as a subcontractor to Veit USA, was tasked with removing vast amounts of wood waste which had sat at the bottom of the river for more than a century.
“In the late 1800s, this part of the waterfront was the home to a couple of sawmills and, as was common in those days, cuttings from the mills’ operations ended up in the river — that’s just the way things were done back then,” said Gilbertson. “Unfortunately that debris, coupled with ongoing sediment deposits, has affected fish and wildlife habitat. By removing the wood waste and building a small island in the Grassy point area, the DNR hopes to restore the damaged habitat and help fish and other wildlife thrive.”
To put the scope of the wood removal effort into perspective, MAE’s foreman, Matt Brink, said that, less than halfway into the project, they’d already pulled out more than 100,000 cu. yd. of material from the river bottom. And, if such work conjures up images of soggy, decayed muck, nothing could be further from the truth.
“We are pulling up logs that are in amazingly great shape for being submerged for more than a century,” he said. “In fact, we’ve hit several pockets of material in which sawdust has come out relatively dry and fluffy — not what we’d expected to find at all.”
As mentioned, MAE’s past projects have included wetland mitigation and swamp work in which the machine operator could see where they we were digging. They were also projects in which maintaining accurate river or lake bottom elevations was not that critical. Such was not the case at Grassy Point, said Gilbertson.
“Here, inches really matter, both from a compliancy and a materials standpoint,” he said. “Simply put, we won’t get paid for any material we over dig, but it could cost us dearly if we were to under dig. Given that we can see less than a foot into the murky water, it quickly became obvious we needed a more precise method of measuring our cuts as we removed debris.”
The Deal, McCoy
Based on his past construction experience, Gilbertson suspected that the answer to his “digging blind” dilemma could be found in a GPS solution. Armed only with that general feeling, he contacted the Grand Rapids branch of McCoy Construction and Forestry, the local John Deere dealer to explore his options. According to Lucas Weir, McCoy’s IGS specialist, it was a call that would change the way in which Gilbertson and his team would work moving forward.
“I came into the office and was told they’d gotten a call from a guy who works with excavators in the swamps and they want to put GPS on them,” he said. “And oh, can you do it by next week? So I went out and met with Steve and, after hearing his concerns, I suggested a Topcon HiPer VR with an FC-5000 field controller, as well as a X-53i system on their excavator. Working with our partner dealer, the Bloomington, Minnesota branch of RDO Integrated Controls, we got it all for him in short order.”
“Luke and the team at McCoy have been patient in getting us up to speed and the change for us has been dramatic,” said Gilbertson. “I can’t imagine where GPS could be more helpful than under water. On a traditional land-based operation, you can look at an area and immediately see: ‘Oh that’s high; we left a bunch out there that needs to be taken off.’ But once the water removes that visual element from the equation, it’s a whole new ballgame. In addition, the Topcon system is also set up to measure as-builts as the operator digs. It is the ideal solution for us.”
Gilbertson’s focus on getting it right the first time is driven by the fact that their fee for the Grassy Point project is based on a unit price for the material recovered. If they were to undercut by six inches, for example, over the course of the six-acre job that translates to 4,500 yards — or roughly $100,000 — for which they would not be compensated.
“Conversely, if we dig six inches too deep, we will not be paid for removing that additional material,” he said. “So, there’s the potential for a couple hundred thousand dollars that we could lose by not accurately knowing the surface we are dealing with. Now, however, the Topcon solution lets my guys know exactly where the bucket is in relation to the plan provided by the engineers. There is no guesswork; it is dead-on every time, with tolerances to 1/10 of a foot — far closer than we need it to be.”
"With the click of a button I can do everything from verifying a machine’s position to sending the as-built back to the office to looking at their screen to answer a question the operator might have about the project itself."
CEO Steve Gilbertson, Midwest Amphibious Equipment (MAE)
Seeing Success in 3D
Though he says the Topcon excavator solution is designed to be inherently user-friendly, McCoy’s Luke Weir said he has been impressed by MAE’s quick grasp of the overall GNSS environment. At the nine-month mark in the project, he said, their knowledge and utilization is at par with where most others are at 18-months.
“Both Steve and Matt Brink, his foreman, have really taken to the technology,” he said. “In fact, not long after that first system was installed, their situation went from: ‘We need to be able to see what we’re doing under water,’ to ‘Can we do as-builts?’ to ‘We need an efficient way to monitor progress and generate reports right from the office.’ In short order, they went from nothing, to a nice package of solutions that included an indicate GPS system on two excavators, a pair of base/rover setups and Topcon Sitelink3D.”
The issues of seeing underwater and generating as-builts were immediately solved with the addition of GPS to the excavators. The last component was addressed through Sitelink3D, a point-to-point communications solution. According to Gilbertson, the nature of their work — primarily in remote, swampy locations — means access to his machines can be challenging at best, sometimes near impossible.
“If I am at a mitigation site, there might be several miles between machines — just getting to two machines in a day to see what they are doing is a real chore. Instead, with the click of a button I can do everything from verifying a machine’s position to sending the as-built back to the office to looking at their screen to answer a question the operator might have about the project itself. We’ve only scratched the surface of what can be done with Sitelink, but it’s still proving a really nice addition to our operation.”
Taking it to the Mat
In addition to the efficiency afforded by its newfound GNSS tools, MAE is in a strong position to challenge the status quo for work in challenging, swampy areas. The traditional method for getting heavy equipment into such areas, laying down a continuous series of hardwood excavator mats, is an expensive proposition, with costs that can quickly mount if a project is delayed for any reason.
“However, our services, despite being far less-costly in the long run, are still a tough sell when a contractor has a million dollars worth of mats in his yard, as some of the larger companies do,” said Gilbertson. “But we’re working at changing that. On a potential project for a large pipeline company that needs some pipe removed, I estimate their matting charge to be $300,000 to $350,000 per mile — per month. My total costs with our machines would be about $400,000 a mile to do it; that’s roughly a 30-40% savings. So the numbers are there, particularly now when we can be faster and more efficient. We have to show these companies that it is definitely time to look at an alternative approach to doing things.”
Even before acquiring the GNSS solutions, MAE was turning heads just by nature of its ability to bypass the need for mats. Nowhere was that more evident than on a cleanup project this past winter that was part of the Great Northern Transmission Line southward from Manitoba, Canada to Grand Rapids, Minn. According to Gilbertson, another company was already out on the job with an excavator, painstakingly leapfrogging mats to move forward, when the utility company called and asked if MAE could do it.
“We put in at the town of Effie in mid-October and the contract called for us to do 18 miles of cleanup to Big Falls,” he said. “They wanted it done by the end of December with a 10-day off-period for deer season. Four weeks later, when we called asking if there was anything else they needed us to do, they asked where we were and were stunned to find out we’d already reached Big Falls — even before the deer season break. We did that distance in such a short period of time because were able to work in the right-of-way, while the other company, on mats, did only a couple of miles. While we might have been more expensive up front, it ultimately saved them a lot of time and money.”
He added that he is a expecting similar reaction after their work at Grassy Point wraps up. Though they encountered some delays this past spring, they are on pace for an on-time completion, if not a bit ahead of schedule.
“What’s even more impressive, however, is that our contract now is almost 1.5 times larger than when we started, and a good deal of the credit for that has to go to the Topcon solutions allowing us to be so much more productive and land the additional work.”
A Nice Catch
He added that the new technology has given them the confidence, not only to bid additional work like the Grassy Point project, but also to better manage the work they currently have. To illustrate, he cites a discrepancy they recently uncovered that could have proven costly.
“There was an area in which we started digging and saw that we had already reached the halfway point in our quantities, yet it was obvious we were not halfway through the project. So, we did a surface calculation from the topo to the as-built and saw that it was off by 7,500 yards. Without the verification, I might have just dug and moved on, assuming that we removed 21,000 yards when, in reality, we did 28,500 yards. That’s the value these solutions bring to the job; that one catch will pay for everything we’ve invested in GPS to this date. In a very short time we’ve figured out how critical this technology is to our future success. We’re going to embrace it and let the results speak for themselves.”